Summary
- Airbus has a "Dark cockpit" philosophy with blank buttons, while Boeing uses traditional ON/OFF lights for push buttons.
- Airbus uses ECAM for system monitoring and provides see-and-do checklists, while Boeing uses EICAS, which only alerts pilots of failures.
- Airbus has a digital fly-by-wire system with no speed stability, while Boeing has artificial speed stability and manual trim.
Europe-based Airbus and US-based Boeing are the two largest aircraft manufacturers. While most of their commercial aircraft designs look similar to the outside eye, certain operational features differentiate the two manufacturers. For example, one features a side stick controller in the cockpit, while the other has a yoke. Similarly, one has a tray table while the other doesn't.
These are only some of the most obvious differences. But have you ever wondered if there are other technical differences between the two manufacturing philosophies? What operational characteristics do airlines look at when selecting one of the other? This article explores technical differences between the two designs and how they make each one unique in their missions.
Differences in operational philosophy
Airbus was the first manufacturer to develop a Dark cockpit philosophy on their A310s, where the push buttons for various system controls appear blank when operational. This makes it much easier for the pilots to ensure that the systems work as they should. In fact, “all white lights off” is a term used in Airbus documentation when doing the cockpit preparation for the departure.
In Boeing aircraft, the traditional ON light and OFF light for push buttons is still the standard.
ECAM vs EICAS
The ECAM (Electronic centralised aircraft monitoring) is the heart of Airbus aircraft. It monitors various systems in the aircraft, and if a failure occurs, it alerts the pilot. The EICAS (Engine indicating and crew alerting system) is the Boeing counterpart of ECAM. A part of it is used to show engine indications, and it also alerts the flight crew if a failure occurs in a flight.
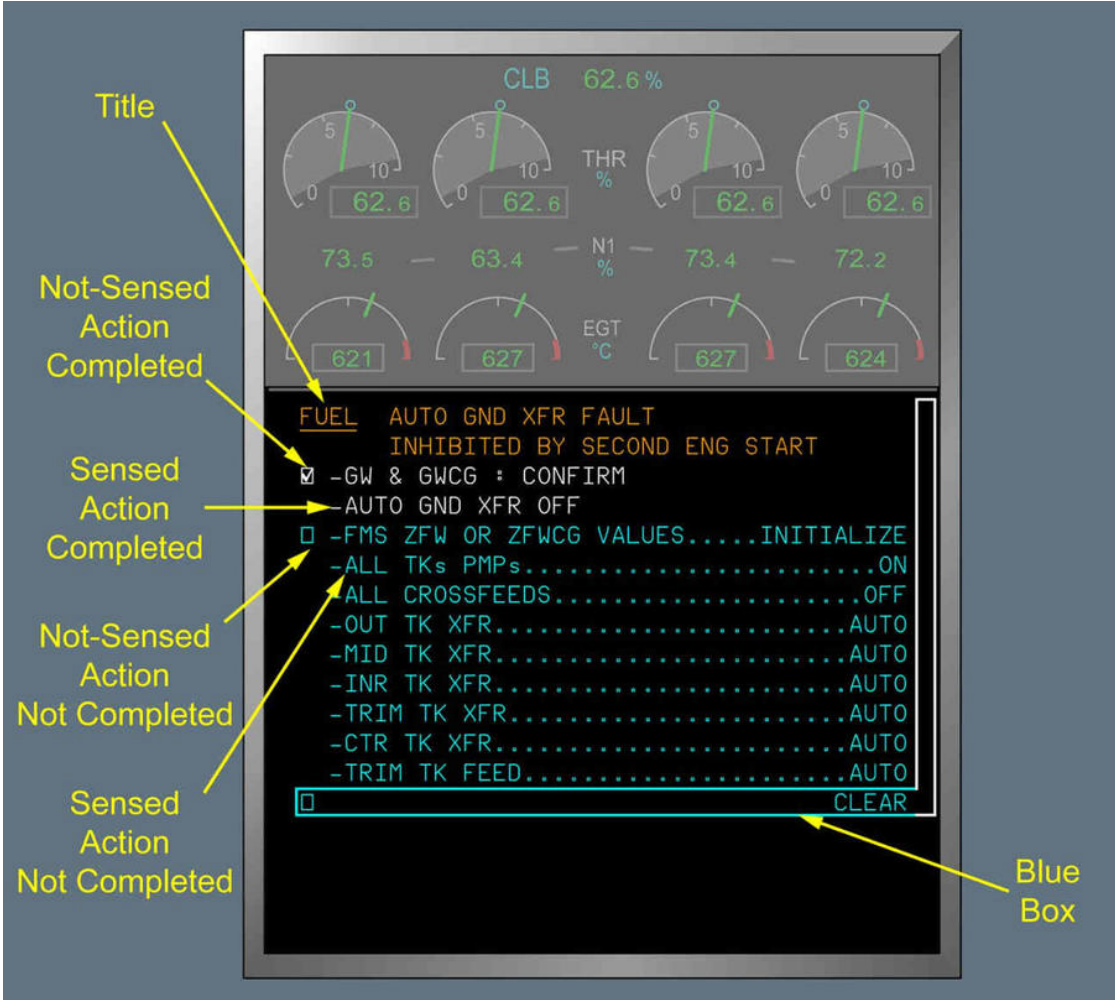
The significant difference between them is that the ECAM is more of a see-and-do system whereby a system's failure is not only alerted to the pilots but an associated electronic non-normal checklist is automatically displayed for the pilots to follow. As the pilots follow the checklist items per the ECAM, the item disappears. For example, in an engine failure event, when the ECAM asks to idle the thrust lever of the failed engine, and the pilot performs that action, the item goes away from the checklist.
The EICAS is simply an alerting system. If a failure occurs, it tells you that failure has occurred. For instance, if an electrical generator fails, the EICAS displays a generator failed message. It does not provide a see-and-do checklist. Once an EICAS message appears, it is the job of the pilots to assess the situation and do the necessary abnormal procedures. In modern Boeing aircraft, electronic checklists are available. However, they must be manually accessed by the pilots.
Fly By Wire (FBW) and flight envelope protection
Airbus aircraft, starting from the A320, have a digital fly-by-wire system, and Boeing's, beginning from the 777, also have fly-by-wire. The Airbus fly-by-wire has no speed stability. It only has pitch stability. A conventional aircraft, due to its natural stability, always tries to return to its trimmed position when pilot input is made on the controls.
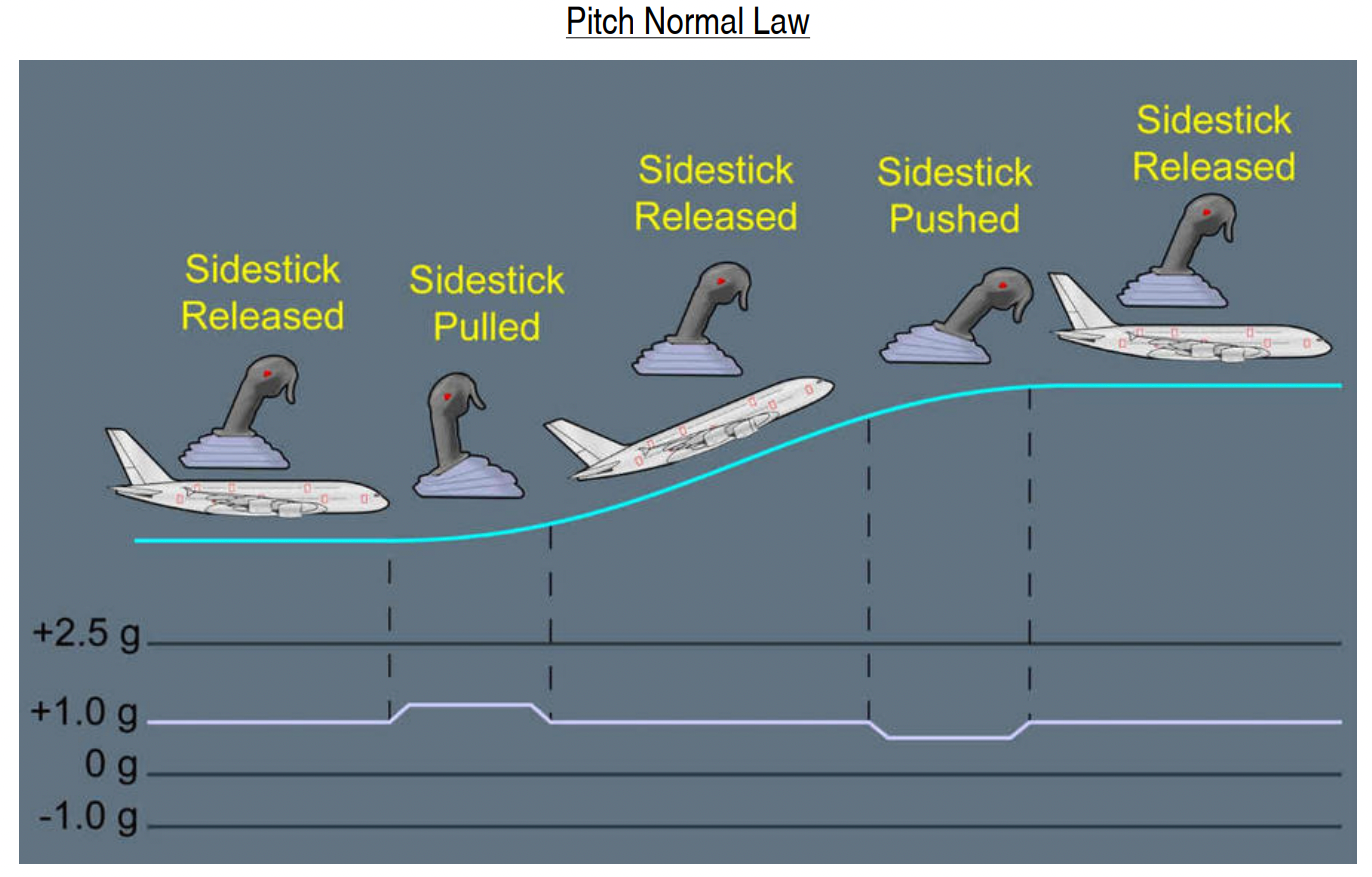
For example, if an aircraft maintains 250 knots and if a pilot pulls back on the controls and leaves it, the aircraft naturally pitches down and up until it stabilizes back at 250 knots. In Airbus aircraft, this does not happen. Airbus designed its aircraft to have neutral stability with automatic trim. If a pilot pulls back on the controls and leaves it, the aircraft maintains the pitch attitude. And it maintains that pitch until the pilot changes the pitch. It does not try to go back to the trimmed state.
Boeing designed their fly-by-wire with artificial speed stability and manual trim. When a Boeing aircraft is disturbed in its trimmed state and let go of the stick, it oscillates up and down like a conventional aircraft until it gains the trimmed state.
On the roll axis, Airbus and Boeing have similar philosophies. When a conventional aircraft is put on a bank, the pilot must constantly pull back on the controls to maintain altitude. But in Airbus and Boeing fly-by-wire, up to a particular bank angle (30 degrees for Boeing and 33 degrees for Airbus), the pilot does not need to compensate for altitude loss as the fly-by-wire system moves the elevator and pitch trim controls as required to maintain the altitude.
Flight control laws
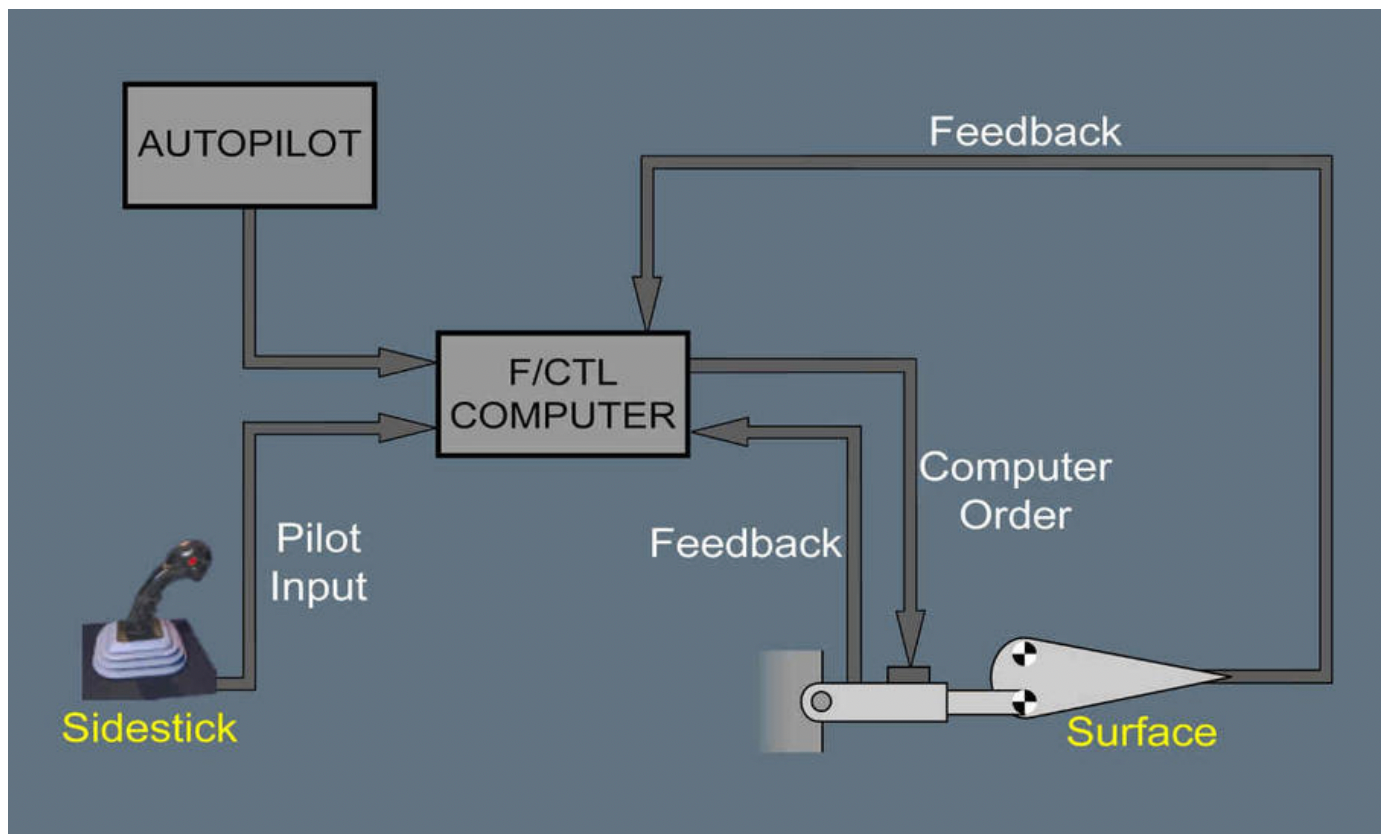
When it comes to flight control laws, Airbus has three: the normal law, the alternate law, and the direct law. Under normal law, the pitch control of the aircraft is a g-load demand. When the pilot moves the stick, he/she demands a certain number of gees and when the stick is released, the computers revert to 1G flight. The pilot does not control the surfaces directly. Also, as previously mentioned, the trimming is achieved automatically.
The roll control, up to 33 degrees of the bank, shows neutral spiral stability, where if a pilot demands a bank angle and releases the stick, the aircraft automatically maintains that angle until changed by the pilot. Beyond 33 degrees, positive spiral stability exists, where if a pilot leaves the stick, the aircraft returns to a bank of 33 degrees.
The yaw control through the rudder is sideslip demand. In older Airbus aircraft, the rudder is not a part of the fly-by-wire.
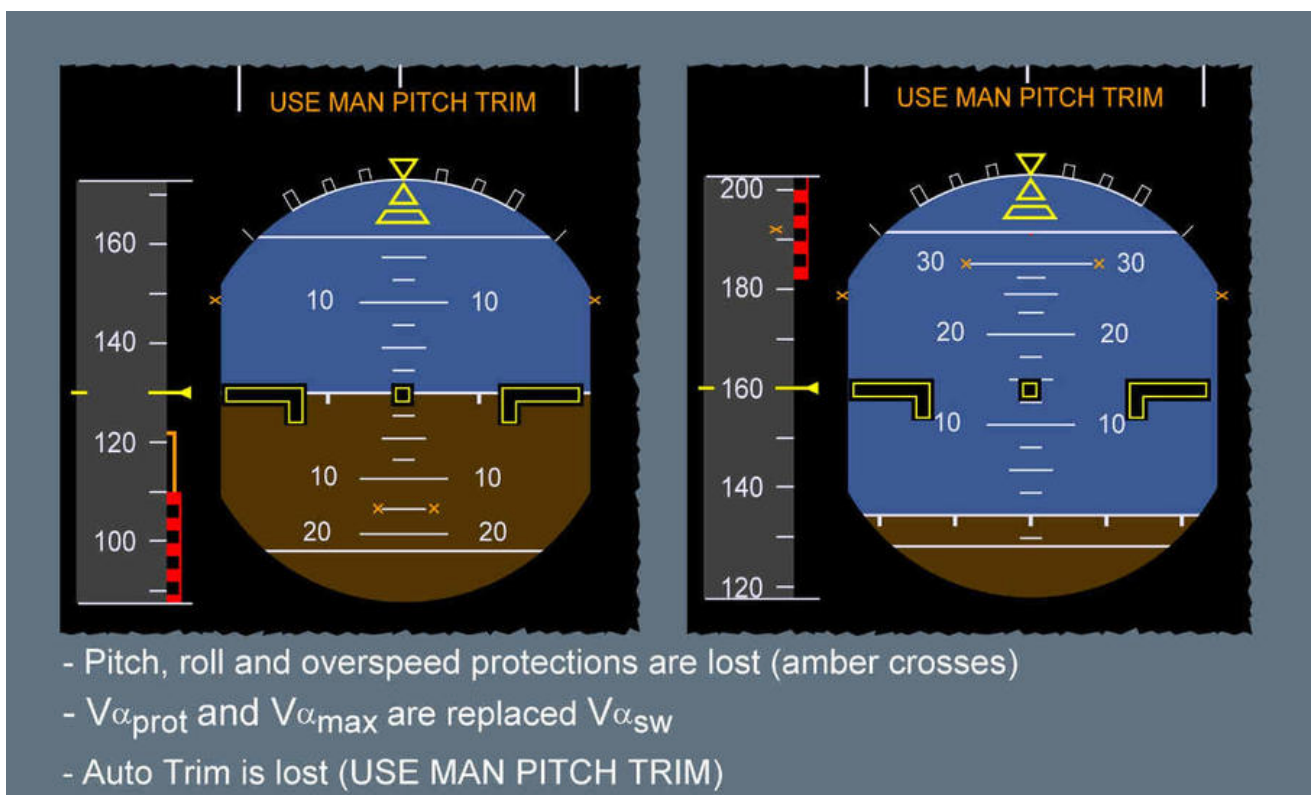
In normal law, all flight envelope protections are also active. When met with certain failure conditions, the aircraft control laws degrade to alternate laws. In alternate law, most of the envelope protections are lost except for the load factor protection. However, in alternate law 1 (first level of alternate law), there exists a high-speed and low-speed stability where if, for instance, the aircraft were to go above the maximum allowable speed (Vmo/Mmo), a gentle nose-up pitch is introduced. In the case of a low-speed situation, a progressive nose-down pitch is introduced by the computers.
If the aircraft systems are degraded further, an alternate law with reduced protections (alternate law 2) is in effect. Here, only load factor protection is active, and the high and low-speed stability is lost. With further failures, the aircraft goes into direct law.
In direct law, all the protections are lost. On the PFD, the message "USE MAN PITCH TRIM" in amber is displayed as the auto trimming function is lost. So, the pilot is required to trim the aircraft manually. When in direct law, there is a direct relationship between side stick deflection and control surface deflection. The maximum elevator deflection given to the pilot is a function of the aircraft CG. It ensures enough control authority with a forward CG and ensures that the controls do not become too sensitive with an aft CG.
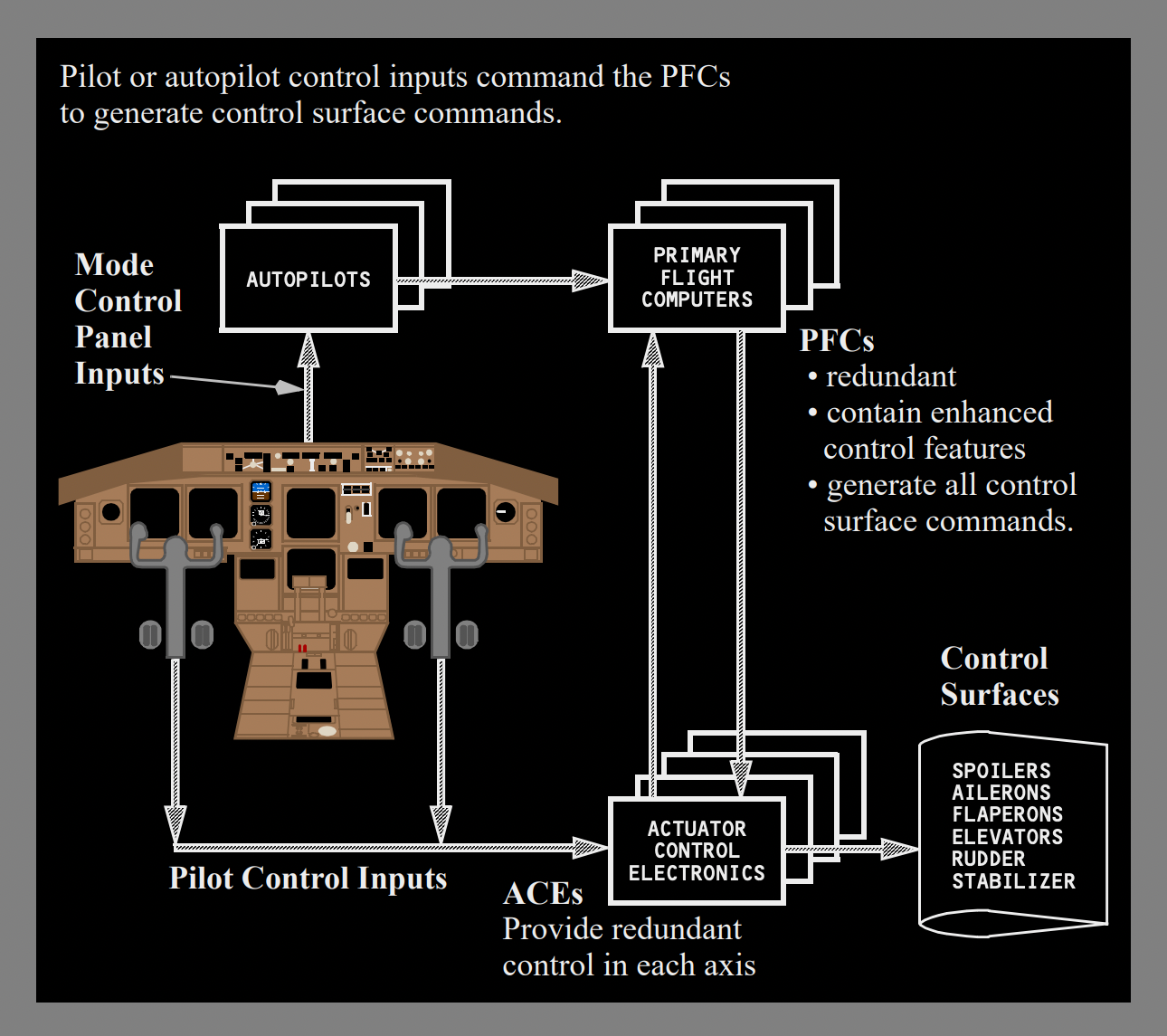
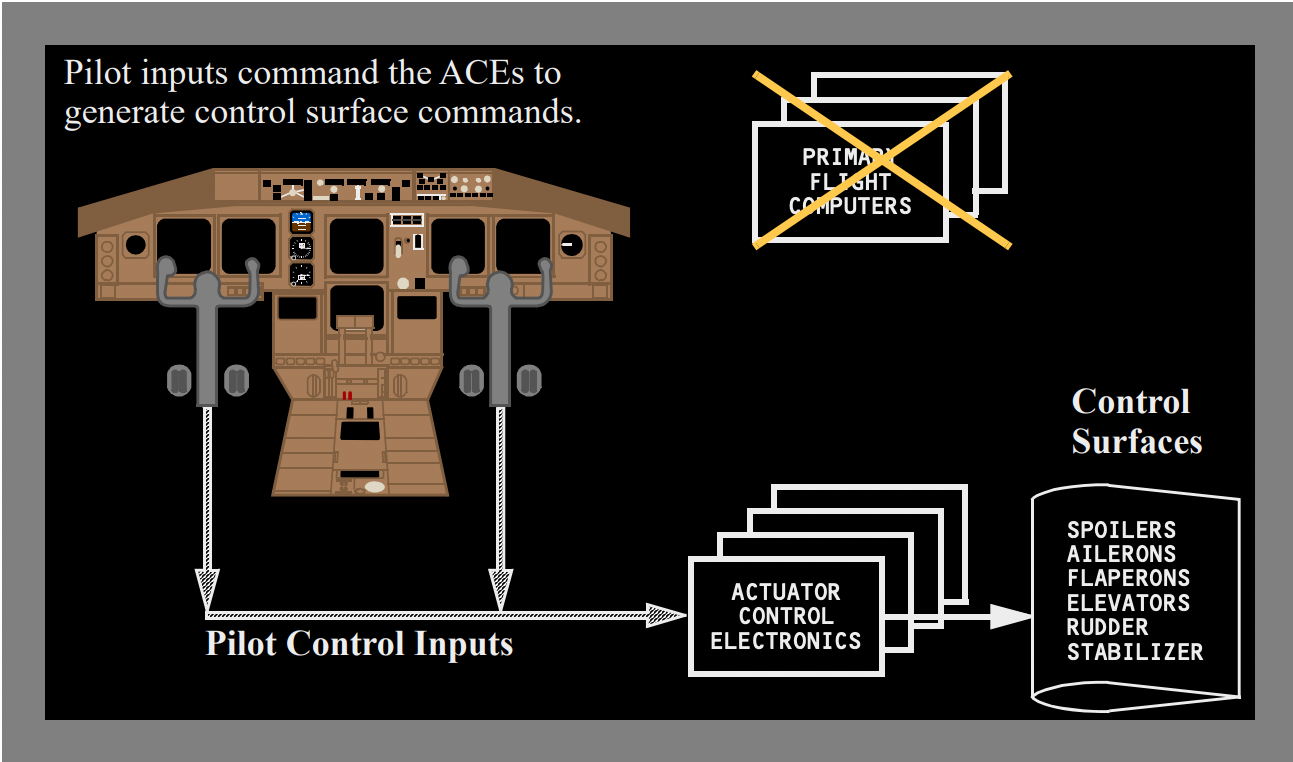
Boeing aircraft also operate in three control modes. They are known as Normal mode, Secondary mode, and Direct mode. The big difference between the Airbus and Boeing control laws/ modes is that in the latter when the pilot makes a control input, it is first sent to Actuator Control Electronics (ACEs).
The ACEs then send it to the Primary Flight Computers (PECs), where the pilot inputs are verified and sent back to the ACEs to command the hydraulic actuators of the flight controls. Airbus has one flight control computer, and the pilot signals it directly to move the controls as per the set control law.
In normal mode, the pilot does not directly control the control surface on the pitch axis. He/she gives a pitch maneuver. The computers then move the elevator to meet the pitch maneuver. As the aircraft has artificial speed stability, a pitch change usually requires manual trimming.
The roll control in normal mode is quite conventional in that the ailerons and flaperon deflections are directly proportional to control wheel displacement. The yaw controls also behave conventionally. That is, the rudder deflection determines the yaw rate.
When the aircraft undergoes failure conditions, it reverts to secondary mode. In secondary mode, the control behavior in pitch is such that the control column and the elevator deflection are directly proportional. The roll and yaw controls are similar to normal mode.
When in secondary mode, all envelope protections are lost, and due to simplified control laws of secondary mode, the handling qualities of the airplane are a little degraded. With further failures, the controls go into direct mode.
In direct mode, the control signals are no longer processed by the PFCs. They go to the ACEs and displace the control surfaces like a conventional aircraft.
The major difference in control laws between Airbus and Boeing is that in normal law, Airbus aircraft have hard protections that the pilots cannot exceed. In Boeing aircraft, the envelope protection is soft. They can be exceeded, but that requires extra pilot effort on the controls.
One of the most controversial points of Airbus aircraft is the claim that the pilots do not have the authority to exceed the flight envelope. However, there are methods by which the pilots could turn off protections if required. In most cases, the flight control computers switch off the protection and degrade the control laws when certain flight parameters are exceeded to allow the pilot to get out of an undesired aircraft state.
Unlike Airbus, Boeing aircraft have interconnected flight control columns. This means that when one pilot moves the controls, the other moves, giving the other pilot tactile feedback. In Airbus planes, the side sticks are not interconnected. Boeing aircraft also have an artificial feel system that increases the stick forces with an increase in speed, like a conventional aircraft. Airbus side sticks also have a feel system made of springs and dampers, but it does not change with speed. The feel is adjusted to mimic what a pilot feels during take-off and landing closely.
Cockpit differences
The most significant difference between a Boeing and an Airbus cockpit is that Boeing uses a conventional yoke, and Airbus uses a side stick. According to Airbus, the side stick makes it easier to fly the aircraft because, with armrests correctly set, only excellent wrist movements are required to maneuver the aircraft. The side stick also gives an unobstructed view of the flight instruments. Boeing believes in tradition, and according to them, the yoke gives the aircraft a better feel.
The other major difference is found in the thrust levers or the throttles. In a Boeing aircraft, the autothrottle is back-driven. On Airbus, the thrust levers do not move. The levers are set at detents, and the computers set the required thrust when the autothrust is on. With the autothrust off, the levers can be manually moved by the pilot.
Why the difference? In the olden days, computers used to move the throttles physically to the desired throttle angle. This was how the autothrottle system worked. These days, the engines are controlled directly by computers, and they can demand the engines to generate a particular amount of thrust without moving the thrust levers. The inside workings of both the Airbus and Boeing throttles are the same.
However, Boeing decided to put motors in their throttles, which moves them to give pilots tactile feedback. Airbus claims this is unnecessary as, according to them, the pilots should use engine instruments to know what the engines are doing rather than using a moving throttle to determine what is happening to the engines.
Similar to the throttles, Boeing also made things like the speed brake levers move when they automatically operate during landings. Airbus speed brake levers remain static.
So, which is better - Boeing or Airbus?
There is no perfect answer to this question. Neither Boeing nor Airbus is better than the other. They both try to achieve a common goal with very different philosophies and are thriving. There are many features in an Airbus that would be nice on a Boeing, and similarly, there are many features in a Boeing that would be pretty enjoyable on an Airbus.
What are your thoughts on the technical differences between the two aircraft types? Which one is your favorite as a pilot? Share your experience in the comments section.






.jpg)